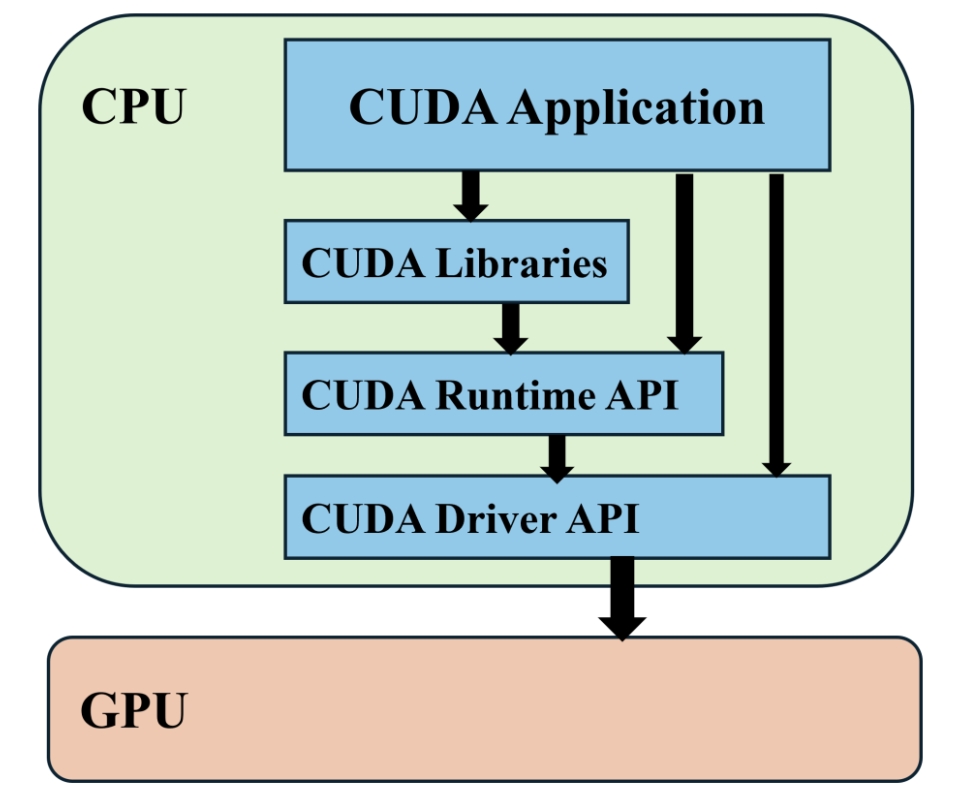
GPU资源共享/抢占
GPU共享的整体架构
这个项目是一个Kubernetes GPU共享调度系统,通过两种类型的pod实现GPU资源共享:
1. Shadow Pod(影子Pod)
- 作用:占用物理GPU资源,作为GPU的实际持有者
- 特征:运行一个简单的sleep容器,不执行实际计算任务
- 创建时机:当quota资源不足时自动创建
- 生命周期:由shadow controller管理,根据使用情况自动创建和删除
2. Share Pod(共享Pod)
- 作用:实际执行计算任务的pod,通过device plugin共享shadow pod的GPU资源
- 特征:使用虚拟GPU设备,通过时间片或空间分割方式共享物理GPU
- 资源请求:请求共享GPU资源(如mizar.share.gpu.2表示2路共享)
核心逻辑链路
1. 配额管理(Quota Controller)
- 监控quota资源状态,计算shadow resource需求
- 维护shadow pod与物理GPU的映射关系
- 处理shadow pod的创建和删除逻辑
2. Shadow Pod管理(Shadow Controller)
- 创建逻辑:当quota的ready + pipelining数量为负值时,计算需要创建的shadow pod数量
- 删除逻辑:根据shadow pod的空闲时间决定是否删除
- 条件检查:通过PodInUsing条件跟踪GPU使用状态
3. 设备插件(Device Plugin)
- Share Device Plugin:为share pod提供虚拟GPU设备
- 设备ID格式:
{namespace}/{shadowpod-name}-{index} - 动态更新设备列表,反映当前可用的shadow pod资源
4. 调度器(Solver)
- ShareGPU Solver:处理share pod事件,管理share pod与shadow pod的绑定关系
- SpotGPU Solver:处理spot pod事件,支持低功耗模式和抢占机制
5. 缓存系统(Mapping Cache)
- 维护三层映射关系:
- Shadow pod → 物理GPU设备
- Share pod → Shadow pod
- 设备状态跟踪(健康、使用中、空闲)
工作流程
- 资源申请:用户创建请求共享GPU的pod(share pod)
- 配额检查:quota controller检查当前资源是否充足
- Shadow Pod创建:如果资源不足,shadow controller创建shadow pod占用物理GPU
- 设备注册:device plugin将shadow pod的GPU注册为虚拟设备
- Pod调度:share pod被调度到有可用shadow pod的节点
- 资源绑定:shareGPU solver将share pod绑定到具体的shadow pod设备
- 使用监控:通过条件系统和metrics监控GPU使用情况
- 资源回收:当share pod结束或shadow pod空闲超时,自动回收资源
关键技术点
- 时间片共享:通过CUDA MPS或时间分片实现GPU计算资源共享
- 动态调整:根据负载动态创建和删除shadow pod
- 优先级管理:支持低功耗模式和抢占机制
- 状态同步:通过Kubernetes条件和annotation保持状态一致性
这种架构实现了GPU资源的超卖和弹性伸缩,显著提高了GPU利用率,同时保持了与传统Kubernetes调度的兼容性。
Spot资源抢占机制
1. 抢占触发条件
spot资源的抢占主要通过以下几种情况触发:
a) 所有者Pod恢复活跃(主要抢占场景)
1 | // owner pod alive, evict spot |
触发条件:当GPU的原始所有者pod(非低功耗模式)重新变得活跃时,spot pod会被立即驱逐。
b) 低功耗模式抢占
1 | func (s *spotGPUSolver) solveBusy(e detectors.Event) error { |
触发条件:当低功耗pod从空闲状态变为繁忙状态时,会驱逐所有使用其GPU资源的spot pod。
2. 抢占执行方式
a) 容器级别抢占(温和抢占)
1 | func (s *spotGPUSolver) evictProcessFor(e detectors.Event) error { |
特点:通过containerd API直接杀死容器进程,实现快速资源回收。
b) Pod级别抢占(强制抢占)
1 | func (s *spotGPUSolver) evictFor(target string) error { |
特点:通过Kubernetes API删除整个pod,确保资源完全释放。
3. 抢占优先级策略
a) 低功耗模式优先
- 低功耗pod享有最高优先级,不会被spot pod抢占
- 只有低功耗pod才能共享GPU给spot pod使用
- 当低功耗pod需要资源时,spot pod会被立即驱逐
b) 资源预留机制
1 | func (s *spotGPUSolver) evictByDevice(e detectors.Event) error { |
4. 抢占后的状态管理
a) 缓存清理
1 | // 更新缓存 |
b) 条件更新
1 | // 更新活跃条件 |
c) 指标记录
1 | // 更新驱逐计数器 |
5. 抢占策略特点
- 实时性:通过事件驱动机制,实时响应资源状态变化
- 分级处理:先尝试容器级温和抢占,必要时进行pod级强制抢占
- 状态一致性:确保缓存、设备插件、Kubernetes状态的一致性
- 可观测性:记录详细的抢占日志和指标,便于监控和调试
- 资源保障:优先保障高优先级任务(低功耗pod)的资源需求
这种抢占机制确保了GPU资源的高效利用,同时在需要时能够快速回收资源给高优先级任务使用。
根据ShadowPod生成对应的虚拟设备"的实现流程如下:
1. ShadowPod创建阶段
- 控制器检测需求:
pkg/controllers/shadow/controller.go中的doOneReconcile()方法定期检查配额设备状态 - 创建ShadowPod:当配额不足时,调用
createShadow()方法创建ShadowPod - 生成Pod配置:
generateShadowPod()函数创建包含GPU资源请求的ShadowPod
2. 虚拟设备生成阶段
- 设备检测:
pkg/detectors/shadow/shadow.go中的init()方法根据ShadowPod的share spec生成虚拟设备ID - 设备ID格式:每个ShadowPod生成多个虚拟设备ID,格式为
{namespace}/{podname}-{index}(如default/shadowpod-abc123-0) - 设备状态生成:
GenerateDeviceStatus()函数创建设备状态信息
3. 设备插件注册阶段
- 设备初始化:
pkg/deviceplugin/share/deviceplugin.go中的initDevices()方法扫描所有ShadowPod并初始化设备列表 - 设备注册:通过Kubernetes Device Plugin接口向kubelet注册虚拟设备
4. 设备分配阶段
- 设备分配:
pkg/deviceplugin/share/stub.go中的Allocate()方法处理设备分配请求 - 设备映射:为容器生成设备映射注解,格式为
mizar.k8s.io/container-devices-from.{container}
5. 核心机制
- Share Spec映射:根据share spec值(2、4、8、16)映射到对应的物理GPU数量
- 设备生命周期管理:通过缓存机制(
pkg/apis/mapping_cache.go)管理设备状态 - 配额隔离:确保每个租户只能使用自己配额内的虚拟设备
整个流程实现了从ShadowPod创建到虚拟设备生成、注册、分配的全链路自动化管理,为Kubernetes集群提供了GPU资源共享能力。
Share GPU数量与ShadowPod虚拟设备的关系
1. Share Spec映射关系
在 pkg/controllers/shadow/shadow.go 中定义了share spec到物理GPU数量的映射:
1 | var gpuCountMapping map[int]int = map[int]int{ |
2. ShadowPod创建虚拟设备
- 虚拟设备生成:在
pkg/detectors/shadow/shadow.go中,每个ShadowPod根据share spec生成多个虚拟设备ID - 设备ID格式:
{namespace}/{podname}-{index}(如default/shadowpod-abc123-0) - 设备数量:share spec值决定生成的虚拟设备数量
3. 虚拟设备到真实显卡的映射
对于Share设备(非Spot):
- 设备注册:虚拟设备通过Kubernetes Device Plugin接口注册到kubelet
- 容器注解:在
pkg/deviceplugin/share/stub.go中,为容器生成设备映射注解:1
2
3
4
5{
"_/shadowpod-name/main": {
"*": ["shadowpod-name-0", "shadowpod-name-1"]
}
} - 运行时映射:容器运行时(如containerd)根据注解将虚拟设备映射到容器内
对于Spot设备:
- 真实设备发现:在
pkg/deviceplugin/spot/deviceplugin.go中,通过连接真实的NVIDIA设备插件获取物理GPU ID - ID转换:使用
utils.OriginalID_To_SpotID()将物理GPU ID转换为spot设备ID(添加"-spot"后缀) - 设备映射:在
pkg/deviceplugin/spot/stub.go中,为容器生成包含真实设备ID的注解:1
2
3{
"nvidia.com/gpu": ["GPU-abc123", "GPU-def456"]
}
4. 核心映射机制
- 缓存管理:
pkg/apis/mapping_cache.go管理设备所有权和使用关系 - 设备分配:通过Kubernetes Device Plugin协议进行设备分配
- 运行时注入:容器运行时根据设备注解将对应的物理设备注入到容器中
5. 使用流程
- ShadowPod创建时申请物理GPU资源
- 根据share spec生成对应数量的虚拟设备
- Share Pod使用时,虚拟设备通过容器注解映射到对应的物理GPU
- 容器运行时将物理GPU设备挂载到容器内
这种设计实现了GPU资源的细粒度共享,多个Pod可以共享同一物理GPU的不同计算单元。
虚拟设备到真实物理设备的映射机制
1. 核心原理:Kubernetes Device Plugin + 容器运行时注解
通过Kubernetes Device Plugin机制和容器运行时注解,实现了虚拟设备到真实物理设备的映射。关键在于两个核心注解:
2. Spot设备的真实设备映射
在 pkg/deviceplugin/spot/stub.go 中:
1 | // 生成包含真实设备ID的注解 |
生成的注解示例:
1 | { |
3. Share设备的设备关系映射
在 pkg/deviceplugin/share/stub.go 中:
1 | // 生成设备关系注解 |
生成的注解示例:
1 | { |
4. 容器运行时的设备注入流程
- Kubelet接收设备分配:Kubelet通过Device Plugin接口获取设备分配响应
- 注解传递:Kubelet将设备注解添加到Pod的容器规范中
- 容器运行时处理:容器运行时(如containerd)解析这些特殊注解
- 真实设备挂载:根据注解信息,运行时将对应的物理设备挂载到容器内
5. 关键组件协作
- Device Plugin:提供虚拟设备接口,生成设备映射注解
- Kubelet:接收设备分配请求,传递注解到容器运行时
- 容器运行时:解析注解,执行实际的设备挂载操作
- Mizar运行时组件:处理特殊的设备关系注解,实现设备共享
6. 为什么能在容器内看到真实设备
当容器运行时处理这些注解时:
- 对于Spot设备:直接将注解中的真实GPU设备ID(如
GPU-abc123)挂载到容器内 - 对于Share设备:通过Mizar的运行时组件,将虚拟设备映射到对应的物理GPU计算单元
这样,虽然在Kubernetes层面Pod申请的是虚拟设备,但实际在容器内挂载的是真实的物理设备文件(如/dev/nvidia0),因此可以通过ls /dev看到真实的GPU设备。